Localizing the SDGs: Does the SDG Implementation Require a Reform of the Way the United Nations works? (2/4 posts)
2. Efforts to localize the SDGs (2015 and 2020)
Note on this series of blog posts
The UN Secretary General and others admitted in 2020 that the implementation of the Agenda 2030 and the Sustainable Development Goals SDGs is off track. To put it back on track there is an urgent need to improve and accelerate implementation of SDG. But does that include local action only or does it need also an improved enabling environment and would that require changes in the way the UN and the member states work? Guided by this question I am launching with the next week on my new blog 'With burning patience' a series of four posts on this burning issue of localizing and implementing the SDG.
Post 1: The UN in 2015 prepared the SDG but no appropriate enabling environment and implementation mechanism
Post 2: Efforts to localize the SDG (2015-2020)
Post 3: Local actors call for a seat at the table of international decision-makers to improve SDG implementation (public on 11 Jan 21 or earlier)
Post 4: Does localizing SDG require a reform of the way the United Nations works? (public on 13 Jan 21 or earlier)
To read all posts of the blog 'With burning patience' please follow this link
https://www.ugraute.de/blog-1
The challenge of implementing SDGs with unclear means of implementation
To write about the SDG localization and implementation is not easy. In deed, many national and local SDG policies, programmes and projects have been launched. In addition, there are numerous progress reports. However, the overall picture is mixed and the success at risk. When presenting the Sustainable Development Goals Report in early 2020 the Secretary-General of the United Nations António Guterres summarized the situation as follows:
The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2020 brings together the latest data to show us that, before the COVID-19 pandemic, progress remained uneven and we were not on track to meet the Goals by 2030. Some gains were visible: the share of children and youth out of school had fallen; the incidence of many communicable diseases was in decline; access to safely managed drinking water had improved; and women’s representation in leadership roles was increasing. At the same time, the number of people suffering from food insecurity was on the rise, the natural environment continued to deteriorate at an alarming rate, and dramatic levels of inequality persisted in all regions. Change was still not happening at the speed or scale required. [1]
In spite of available Thematic and SDG Reviews, Voluntary National Reviews (VNR) and complimentary Voluntary Local Reviews delivered it remains difficult to get a full picture of the state of implementation and to outline the ideal enabling environment and procedures to implement the Agenda 2030 and its SDGs.[2] VNR are no independent reports but voluntary reports by national governments. It is the exception that a country, like Germany in 2016, develops its VNR together with civil society and private sector representatives. In case of Germany the country even shared the speaking slot at the High Level Political Forum (HLPF) with civil society. But even here it is still the view of one country and not an independent external monitoring or evaluation. Unfortunately, at the end of the predecessor agendas, i.e. the Millennium Development Goals (MDG) and the Rio Process which followed the UN Conference in Rio de Janeiro in 1992, no thorough evaluation was carried out. Therefore, at the end of MDG and Rio Process in 2015 the member states took their decision to launch the new Agenda 2030 without being informed by a thorough evaluation of MDG and Rio Process. And now in early 2021 we again only now that there is not enough progress but there are no clear recommendation how to change that. Member states still see no need to develop and adopt a result based implementation mechanism for the Agenda 2030. Instead, the implementation was delegated to the member states and its up to member states when they come up with a VNR.
This all is a pity because part of the resolutions of the Rio Conference in 1992 was the Local Agenda 21. 6400 local initiatives in 183 countries have been launched with reference to the Local Agenda 21 aiming at mainstreaming sustainable thinking and action. Not all of them were successful and only few exist until today but for the localization of SDG a thorough evaluation of the Local Agenda initiatives would have been an enormous treasure. Especially a better understanding on how many of them failed would be helpful to set up the implementation structure to localize SDG. [3]
Without a proper implementation structure, necessary resources and monitoring indicators member states and the UN embarked into the implementation phase. Certainly, the Agenda 2030 was good to protect the sovereignty of member states represented by their national governments but the prize for it is that localization and implementation of SDG became in parts a matter of chance. This is a problem because the Agenda 2030 is crucial for the preservation of life on earth and for our future development. Therefore, it doesn't come at a surprise that the UN Secretary General acknowledged that SDG implementation is off track five years after its launch.
Even the member states already in 2019 were no more satisfied and committed, among other things, to:
“Strengthening the high-level political forum; we pledge to carry out an ambitious and effective review of the format and organizational aspects of the high-level political forum and follow-up and review of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development at the global level during the seventy-fourth session of the General Assembly with a view to better addressing gaps in implementation and linking identified challenges with appropriate responses, including on financing, to further strengthen the effective and participatory character of this intergovernmental forum and encourage the peer-learning character of the voluntary national reviews.”[4]
The German Institute for International and Security Affairs suggested in February 2020 that when celebrating the UN’s 75th anniversary, member states should strengthen the HLPF, as the UN’s “home of the SDGs”, ensuring the forum is fit for purpose to support them in their efforts to master the decade of action and delivery. Unfortunately, that statement came about the same time when attention shifted to the Corona pandemic and eventually no reform of the HLPF was adopted at the UN's 75th anniversary summit in September 2020.
But let's not end the blog here with a negative conclusion. Instead, let's indicate some of the guidance materials and tools which were produced either by UN agencies or other stakeholders. They are important as they provide information on what is needed for a successful localization and implementation of SDG. In addition. local stakeholder can use them as guidance when developing their own activities.
[1] United Nations (UN) (2020): The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2020, https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2020/
[2] Compare Voluntary National Reviews Database at https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/vnrs/
Global Environmental Strategies (IGES) (2020): State of Voluntary Local Reviews 2020: Local Action for Global Impact and Achieving the SDGs.
[3] Local Agenda 21 Survey. A Study of Responses by Local Authorities and Their National and International Associations to Agenda 21. ICLEI/UNDPCSD, 1997.
Local Governments’ Response to Agenda 21: Summary Report of Local Agenda 21 Survey with Regional Focus, ICLEI, 2002.
[4] UNGA, Political declaration of the high-level political forum on sustainable development convened under the auspices of the General Assembly (A/RES/74/4) (New York: UN, 15 October 2019), para. 2; Beisheim, Marianne: Reviewing the HLPF’s “format and organizational aspects”– what’s being discussed? Assessing current proposals under debate. German Institute for International and Security Affairs, Working Paper Nr. 1, February 2020.
Guidance Tools to Localize SDGs
In 2016 the Global Taskforce in cooperation with UNDP and UN-Habitat launched the Roadmap for Localizing the SDGs aiming to support local and regional governments and other local stakeholders in implementing the 2030 Agenda at local level. The Roadmap reflects the voluntary character of the Agenda 2030 and SDGs. It doesn't provide advise on formal procedures to set up implementing structures, funding provisions and rules for accountability and transparency. Instead, it has a strong supply orientation and appeal character and wants to motivate and provide support to local stakeholders interested in implementing the agenda.
The Roadmap is composed of five parts:
- Awareness-raising
- Advocacy
- Implementation
- Monitoring
- Where do we go from here? as a forward looking final section
Important is also the work done with a focus on world regions. To be mentioned is for instance an initiative of PLATFORMA and the Council of European Municipalities and Regions (CEMR). They launched in cooperation with UCLG in July 2020 the study 'THE 2030 AGENDA Through the eyes of local and regional governments’ association'.[1] Already in November 2008 in Marseille, European Ministers responsible for urban development endorsed the creation of a common European Reference Framework for Sustainable Cities (RFSC). Today RFSC provides a web application to guide cities on their own path towards sustainability (visit www.rfsc.eu).
Also very active is the Asia and Pacific region. I recall reviewing the draft of the publication 'THE FUTURE OF ASIAN & PACIFIC CITIES Transformative Pathways Towards Sustainable Urban Development' published by ESCAP and UN-Habitat in 2019.
The "report is an attempt to reimagine the urban future. It projects a picture of a future that is prosperous, resilient and inclusive. It analyses possibilities for sustainable development by asking what kind of policy options could help cities in the region localize and meet the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development." [2]
The roadmaps, guidebooks, studies and other sources not mentioned here are important even if the enabling environment for SDG implementation is not sufficient. They allow stakeholders at the local level to go ahead and do the local groundwork for a more sustainable development considering the specific context of their municipality and territory. They are all forward looking and aim at fostering efforts to localize SDG.
[1] https://platforma-dev.eu/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/CEMR-PLATFORMA-SDGs-2020-EN-Final.pdf (accessed on 8 January 2021)
[2] https://www.unescap.org/sites/default/d8files/knowledge-products/Future%20of%20AP%20Cities%20Report%
202019.pdf (accessed on 8 January 2021)
International Guidelines on Urban and Territorial Planning (IG-UTP)
Last but not least, I have to mention that there are other guidance documents and toolkits by other organizations. They may have existed already at the time when the Agenda 2030 was launched and sometimes their importance is underrated. One outstanding example is the International Guidelines on Urban and Territorial Planning (IG-UTP). They were adopted by the Governing Council of the United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-Habitat) in spring 2015, i.e. even prior to the adoption of the Agenda 2030 and prior to the adoption of the New Urban Agenda (NUA) at the Habitat III conference in 2016.[1]
In my own advisory work I had to take note more than once that for mayors, urban planners and other local stakeholders it is not always easy to understand why the UN adopted the NUA on top of the Agenda 2030 without clearly linking the two and without a coordinated implementation mechanism for the two. Instead, while it is not easy to implement the NUA, it is a lot easier to communicate the value added of other guidance tools like the IG-UTP which was also produced by experts in the framework of UN-Habitat.
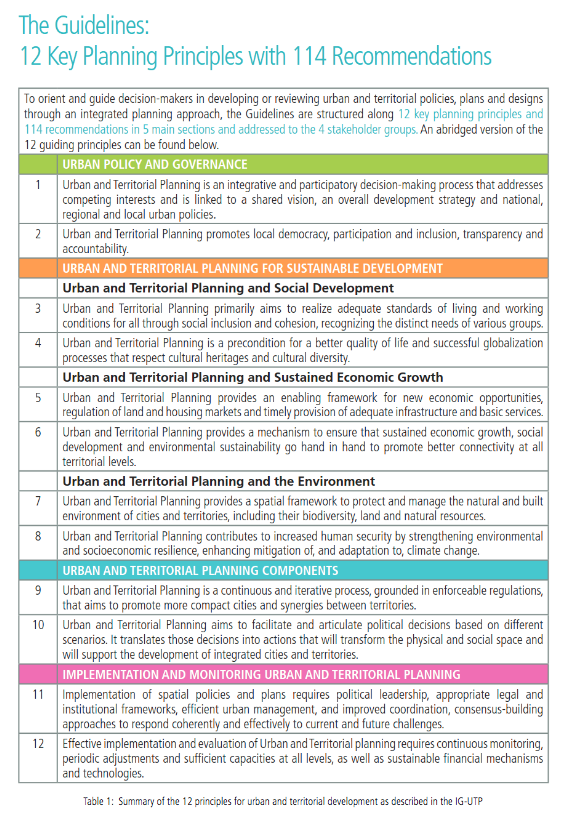
Just have a look at the 12 Key Principles as described in the Guidelines (see table). They provide a snapshot of both, the complexity of challenges and the how to do of integrated planning for sustainable development. With ambitious agendas like Agenda 2030, SDG and NUA there is the challenge of the 'last mile', i.e. the translation of the global agenda and goals into the specific context of a municipality or territory. This is again an issue of the implementation mechanism. It needs to be assured that the implementation of the goals is operational at all levels of governance. SDG (and NUA) are not self-explanatory. The more complex and interrelated global goals the more it is important to translate them into the specific context and day-to-day work situation of local authorities and other stakeholders. In this respect the IG-UTP can help a lot. The Guidelines are no local master plan by themselves but at least its 12 Key Principles and 114 action-oriented recommendations have been developed from a practitioners point of view.
[1] Link to the IG-UTP and IG-UTP Handbook:
https://unhabitat.org/project/international-guidelines-on-urban-and-territorial-planning-guidelines-or-igutp
It will be important to not loose the momentum of the above and other on-going activities because they are indispensable for goals achievement. However, available roadmaps, toolkits and guidelines cannot and don't claim to be a substitute for a proper implementation mechanism and enabling environment. Such mechanisms and enabling environment need to be well thought-out linking the global, national and local parts of the development pillar. And, of course, to support transparency and accountability they need to describe tasks, roles and responsibilities for all actor groups involved.
The next two blog posts will discuss changes proposed to better localize SDG and what that could mean for the way the UN works.
New Paragraph
Policies and Governance for Resilient and Sustainable Cities and Regions